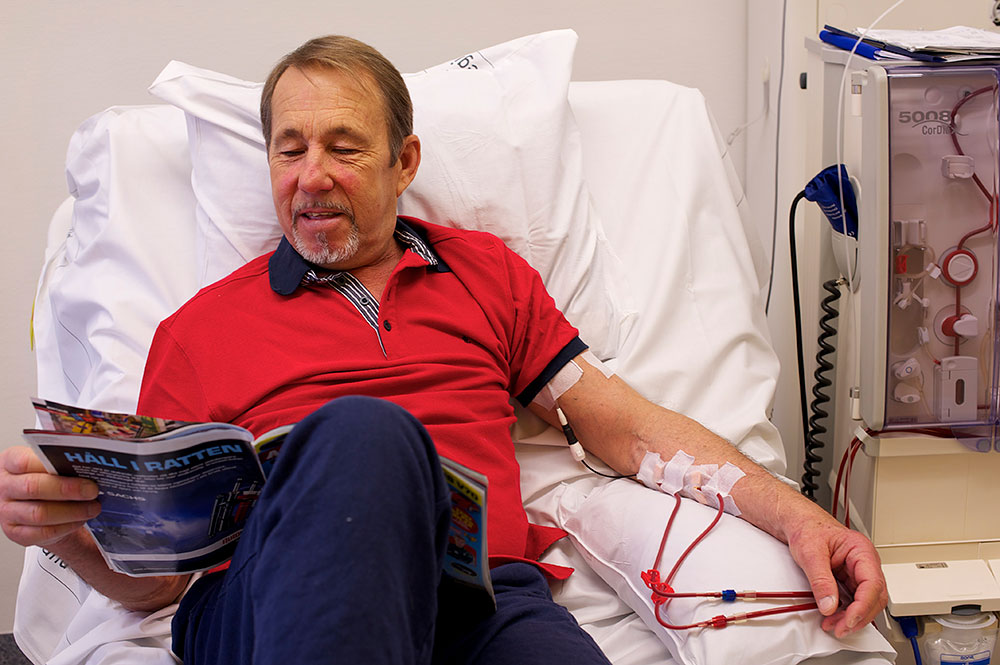
Patients at risk
All hemodialysis patients are exposed to the risks of venous needle dislodgement or catheter leakage and we strongly urge the use of additional safety precautions during dialysis treatments.
Studies have shown that around 20% of patients in center are at a higher risk than others:
- Blanket over access arm
- Elderly with fever
- Confused patients
- Corner position in the unit
- Single patient room
- Self- and night dialysis in center
(NHS Scotland 18 %, Veteran Affairs 22 %)
For home hemodialysis patients and/or night dialysis patients, this counts for 100% of patients as there is no clinical personnel around.
References:
Hawthorne, G., Lightfoot, C. J., Smith, A. C., Khunti, K., Wilkinson, T. J. 2023. Multimorbidity prevalence and patterns in chronic kidney disease: findings from an observational multicentre UK cohort study. Int Urol Nephrol, 55(8), 2047-2057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03516-1
Gupta, A. and Zimmerman, D. 2021. Complications and challenges of home hemodialysis: A historical review. Semin Dial, 34(4), 269-274. https://doi.org/10.1111/sdi.12960
Pauly, R. P., Eastwood, D. O., Marshall, M. R. 2015. Patient safety in home hemodialysis: quality assurance and serious adverse events in the home setting. Hemodial Int, 19 Suppl 1, S59-70. https://doi.org/10.1111/hdi.12248
Ellingson, K. D., Palekar, R. S., Lucero, C. A., Kurkjian, K. M., Chai, S. J., Schlossberg, D. S., D. S.; Vincenti, D. M.; Fink, J. C.; Davies-Cole, J. O.; Magri, J. M.; Arduino, M. J., Patel, P. R. 2012. Vascular access hemorrhages contribute to deaths among hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int, 82(6), 686-692. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2012.185